There are only a few days to go before Christmas. In the UK, like many western countries, people seem geared towards an over-indulgent holiday season. Too much money will be spent on presents. Too much food and drink will be consumed. Too much effort will go into trying to ensure everyone has a wonderful time. Too much time will be spent watching special programmes on TV. And too few will reflect on the birthday of Jesus Christ, the event which should undergird everything we are celebrating.
But I’ve never believed in being a grumbler about Christmas. I enjoy Christmas though I admit that I don’t get close to crazy excited like I did when I was young. I’d wish more people thought about its origins, but even if they don’t it is still a wonderful season, including special time with family and giving and receiving presents.
For this last blog post before Christmas I’ve assembled a miscellany of things about Christmas. Some are serious, some less important. But I hope they’re all interesting. Enjoy reading.
Church or pub on Christmas Day
In the UK, only about 5 per cent of the population attend church regularly. That number may not be exact. Pollsters do not all use the same methods, and definitions of ‘regular church attendance’ aren’t all identical. Nevertheless, I suspect the 5 per cent figure is close to being right. My home nation is predominantly non-churched. Except, that is, at Christmas.
It’s not unusual to see full churches for Christmas Eve midnight services. I used to lead and preach at services like that. They could be eventful if some of those weaving their way home after an evening in the pub decided to join the service. All were welcome but not all were at peace with the world or church decorum.
Fewer attend church on Christmas Day. Other things capture attention, not least keeping children calm while they rip the paper wrappings off presents. Then there’s the massive task of preparing and serving a big meal for family and friends. Turkey is the traditional dish in the UK for a Christmas Day meal.
But ‘Statista’ asked people whether they plan to attend church on Christmas Day or spend their time and money in the pub. The answers they got surprised me. Take a look at the chart comparing church or pub attendance for the USA, UK and Germany.

Clearly the USA has the highest percentage of people who will attend church on Christmas Day – 19 per cent. To my surprise the UK trails by only 3 points at 16 per cent, but Germany scores only 12 per cent. However, what all three nations have in common is that church wins over pub. I don’t know why that happens. My guess is that, for some, there may be a long-observed family tradition of going to church on Christmas Day. Others may pass through church doors for a service of lessons and carols but that will be their one-time attendance until next Christmas. However, of course, most Christmas Day churchgoers are people with a real faith in Jesus. They make a priority of attending church to worship before other events overtake their day.
The odd ancestry of Jesus
Some families have an unkempt uncle, an agonising aunt, or a grouchy grandparent, but Jesus had some really strange ancestors. Certainly Matthew, the writer of the first gospel in the New Testament, did not sanitise his list of Jesus’ forebears.
A few years ago I wrote two blog posts about those ancestors of Jesus. If you haven’t read those posts, I’d encourage you to do so now. I promise they’re interesting, challenging and encouraging. Here are the links:
Why is Christmas on December 25?
Why the 25th of December? Well, the first thing to say is that it’s unlikely that Jesus was born in late December. Scholars point out that shepherds wouldn’t have their flocks out in fields in mid-winter. It would also be a strange season to travel with your heavily pregnant wife back to your hometown to be counted in a census (see the opening verses of Luke’s gospel, chapter 2, for mention of that census). For various reasons biblical scholars mostly consider that sometime between spring and summer is more likely for the time of Jesus’ birth.
What is also interesting is that the date of Jesus’ birth was not celebrated or even considered by the early Christians. Matthew’s and Luke’s gospels carry the story of his birth, but there’s no mention of a date. In fact the date of the Saviour’s birth was never discussed by the church until at least the 2nd century.
Two or three theories are put forward now for why December 25 was later made Jesus’ birthday.
A Roman and Christian historian called Sextus Julius Africanus dated a lot of things. (He was born around 180 and died around 250 AD.) For example, he calculated that creation was complete on March 25, 5499 BC. Sextus stuck with March 25 as the exact date when Jesus was conceived in Mary’s womb. That day had already been considered as the date of Jesus’ crucifixion, and perhaps Sextus thought it appropriate to date Jesus’ conception and death on exactly the same date (not in the same year, of course!). How does that affect the date of Christmas? Think: if Jesus was conceived on March 25, nine months later is December 25. Simple really. Well, it was for Sextus, so for him December 25 was the date Jesus was born.
But there could also be another reason for the date. In 274 AD, the Roman emperor Aurelian marked the rebirth of the Unconquered Sun (Sol Invictus) on December 25. Why then? The 25th was just after the winter solstice, and therefore the beginning of days that would gradually get longer. For Emperor Aurelian, December 25 was when the sun had been reborn so there should be a celebration. Move forward to the next century when Emperor Constantine ruled. He was a convert to Christianity who had made his faith the religion of the empire. In 336, and perhaps because he wanted to wean his empire away from pagan gods, he overlaid the Sol Invictus festival on December 25 by marking that date as the birth of Jesus. Thus December 25 became established in the western Roman empire as what we now call Christmas. January 6 was favoured in the east, and the modern Armenian church continues to mark the January date.
There is a popular, broader idea that the date of Christmas was fixed to replace a variety of pagan feasts held in mid winter. That suggestion was never made until the 12th century, and today’s scholars point out that the early Christians didn’t have any interest in borrowing dates from pagan religions. If anything, they distanced themselves from other faiths.
What we shouldn’t confuse here are two very different things. One is the idea of borrowing the date of Jesus’ birth from pagan religions. The other is adopting traditions for Christmas from those religions. The obvious example of the latter is the use of the Christmas tree, which does seem to have originated in the worship of the Druids. They were Celtic priests who decorated their temples with evergreens as a symbol of everlasting life.[1]
No-one can say with certainty why December 25 became the date for Jesus’ birth. Perhaps thinking of March 25 as Jesus’ conception in Mary’s womb, on the same date as his death during Passover, is what led people to the nine months later date for his birth, but there is no complete evidence to support any theory. Since Victorian times we’ve been bombarded at Christmas with wintry images of reindeer, snow flakes, snow covered trees, and children building snowmen. Then, from 1941, we’ve crooned along with Bing Crosby singing ‘I’m dreaming of a white Christmas’. Who would want to surrender all that for another date? I’d consider it. Australians don’t seem too sad about celebrating Christmas on the beach. I could get used to that too.
For more on the date of Christmas, you’ll find a well-written scholarly article – easily understood by non-scholars – here: https://www.biblicalarchaeology.org/daily/people-cultures-in-the-bible/jesus-historical-jesus/how-december-25-became-christmas/
Victoria, Albert and Christmas trees
Evergreen trees have always been popular because, well, they’re evergreen. Deciduous trees, like oak, chestnut and beech, flourish and then for half the year seem to lose their life. Evergreens are fully alive all the time.
So from the most ancient of times – long before Christianity – people collected evergreen branches to hang over doors and windows. In some cultures those evergreens were thought to shut out demons and other evil spirits, and even illness. During a long, hard winter the green branches were also a reminder that spring would come and plants and crops would grow again.
But how did that become the Christmas tree tradition?
There’s no single answer to that question, but there’s evidence that by the 16th century Christians in Germany were bringing evergreen trees into their homes and decorating them. There’s a story – possibly true – that the famous church reformer, Martin Luther, walked home on a dark but clear winter night feeling awestruck by the bright stars overhead. So he erected a tree in his home, and fastened lighted candles to its branches to recapture something of the magnificence he had seen outside.
That German tradition slowly spread across Europe. But its popularity soared in the mid 1800s when Queen Victoria’s German husband, Albert, had trees erected in Windsor Castle and, in 1848, allowed a front cover painting to appear in The Illustrated London News showing the main tree covered in decorations and surrounded by the Royal Family. Other papers picked up on the story, and it massively influenced upper class customs in Britain and many other countries. Royal fever did its work.

During the following decades and into the 20th century, the tradition of the Christmas tree spread quickly and widely. Across the western world almost all homes had Christmas trees. Local authorities mounted Christmas trees in public squares and on their buildings. Large stores placed trees on their balconies and in the main retail areas. Towns and cities publicised ceremonies of switching on the lights on large Christmas trees in prominent places. For example, since 1933 and continuing now, a large Norway spruce tree has been used for the Rockefeller Center Christmas Tree in New York. The 2024 tree is 74ft (22.5m) tall, 43 ft (13.1m) wide, and weighs about 11 tons (24,250 pounds, 11000kg). After the Christmas period, the tree will be donated to Habitat for Humanity and cut into lengths to help with building homes. In Washington DC the National Christmas Tree is erected near the White House, and its lights switched on by the President and First Lady. Trafalgar Square in London has had a Christmas tree donated by Oslo, Norway, every year since 1947. The 2024 tree is 20 metres (65.6ft) tall and has already been scaled by a protestor dressed as Santa Claus.
For a long time now Alison and I have had only artificial Christmas trees in our home, principally for three reasons: that means a real tree is still growing in the forest; artificial trees leave no mess; they can be used for many years. We follow a common tradition of laying presents around the base of the Christmas tree. When our children were young, those presents sparked curiosity which led to exploration. The children would secretly examine the size and weight of each neatly wrapped present, probably hoping the biggest and heaviest was for them. One thing we never have done or will do is sing around the Christmas tree. The TV series Downton Abbey portrays how the aristocratic family would sing along with their servants beside a giant Christmas tree. We have never done that. Maybe it’s because we don’t have servants. Or because we’re not very tuneful.
‘Once in Royal David’s City’
Every Christmas Eve millions in the UK and around the world tune in to a service of carols broadcast from King’s College, Cambridge. The first TV broadcast was in 1954, and then the service televised regularly from 1963. For over 100 years one tradition at the start of that service has not changed. Since 1919 the opening carol has been Once in Royal David’s City, with the first verse sung unaccompanied by a boy soprano. For that soprano, the thought of your solo being heard around the world must be terrifying. What must make it worse is that no-one knows who will be the soloist until the choirmaster selects one of the sopranos just as the service begins. A nod or pointed finger in your direction, and seconds later your voice penetrates the silence. And millions are listening.
The writer of ‘Once in Royal David’s City’ was born Cecil Frances Humphries in 1818 in County Wicklow, Ireland. ‘Royal David’s City’ wasn’t her only famous hymn – I’ll mention two more shortly. They may surprise you. Keep reading…
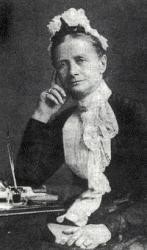
Cecil began writing poems in her school journal from an early age. They were beautifully composed in style and content, and that led to the publication of her first book of poetry called Verses for Seasons, a kind of ‘Christian Year’ of readings for children. That was only the beginning. Overall she wrote more than 400 hymns, basing them on subjects like the Apostles’ Creed, baptism, prayer, the Lord’s Supper and the Ten Commandments. All of them were written in simple language so children could understand and enjoy them.
When Cecil was 30, her book Hymns for Little Children was published. Each hymn was written to bring out the truth of some Christian teaching. Of course, without music the hymns read like poetry. But one year after publication a gifted English organist, Henry John Gauntlett, read Hymns for Little Children, and so loved ‘Once in Royal David’s City’ he composed music for it. As a hymn it was immensely popular and before long it was being sung far and wide.
Its origins as a children’s hymn show by the many direct lessons or references to children in the carol. For example, Cecil writes:
- Christian children all must be / Mild, obedient, good as He.
- For he is our childhood’s pattern; / Day by day, like us He grew;
- And He leads His children on / To the place where He is gone.
- Where like stars His children crowned / All in white shall wait around.
Cecil tells the story of Jesus in the carol, but also applies lessons and truths of the Christian faith for the children who would read or sing it. And that, after all, was her purpose. Hymns for Little Children carries a dedication by Cecil to her godsons, in which she hopes that the language of verse which children love “may help to impress on their minds what they are, what I have promised for them, and what they must seek to be”.

Two years later, in 1850, Cecil married Rev William Alexander (hence her hymns carry the name Cecil Frances Alexander). He eventually became the Anglican Primate of Ireland, a very senior role. Cecil poured her energies into writing hymns but also care for the very poor. The disastrous Irish potato famine – known as the Great Famine or Great Hunger – lasted from 1845-1852.[2] The parishes of Ireland were filled with masses of the disadvantaged. Cecil poured her heart and hands into care for them. Often she’d travel miles in difficult conditions to bring comfort to the sick and poor, and to give them food, medical supplies and warm clothes. Along with her sister, she also founded a school for the deaf.
Cecil wrote many hymns before she died in 1895. One of those was the classic Easter hymn ‘There is a green hill far away’. Another was the hymn loved by children and adults ‘All things bright and beautiful’. Many have regarded Cecil Frances Alexander as one of the greatest hymn writers in the English language.
Eating mince pies at Christmas
There is every good reason to eat mince pies, but no special reason to eat them only at Christmas. They are just as enjoyable at any time of year.

Mince pies date from medieval times but back then they were shaped like a rectangular manger, with a pastry baby Jesus on top. I’d find it hard to bite into that. The round shape of mince pies came only after the Reformation in the 1500s.
People of old linked the ingredients of mince pies with the Christmas story:
- meat (mostly lamb or mutton) represented the shepherds
- dried fruit (raisins, prunes and figs), along with spices (cinnamon, cloves and nutmeg), all expensive items, symbolised the wise men’s gifts
- the mince pies had 13 ingredients in total, equating to Jesus and his 12 disciples.
Eating a mince pie every day of the 12 days of Christmas was thought to bring happiness for the following 12 months.
Around the time of the Reformation, Puritans tried to ban everything associated with Catholicism. That included mince pies. The pies soon made a comeback.
We can all be glad that ban did not last. The popularity of mince pies today is immense. In the UK about 800 million are sold in the run up to Christmas. Add to that the very many which are made in the home. Assuming they’re all eaten, that’s a lot of mince pies and a lot of calories. Some eat none of course – they’re not food for babies, nor does my 102-year-old mother-in-law eat them now. And there are some strange people who don’t like mince pies. A reasonable guess, then, is that those who like mince pies consume an average of between 15 and 19 pies per person at Christmas. Personally I’m a fan of home made pies served warm, and I’m not admitting how many I eat each year.
Finally…
I can’t finish without saying that, for me, Christmas isn’t about carols, mince pies, or presents around a Christmas tree. It is about Jesus, God’s Son, entering this world. No other birth changed the world like his.
My hope and prayer every Christmas is that people will think carefully about the one whose birth began it all (whatever the precise date). I wish you the happiest of Christmases and a new year ahead with many reasons to be thankful.
[1] https://www.history.com/topics/christmas/history-of-christmas-trees
[2] History.com records the famine’s toll: “Before it ended in 1852, the Potato Famine resulted in the death of roughly one million Irish from starvation and related causes, with at least another million forced to leave their homeland as refugees.” For a fuller description of the famine, see: https://www.history.com/topics/immigration/irish-potato-famine